Evidence Based

The disorder known as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is well-known for its effects on impulse control and concentration. While managing ADHD is known to provide obstacles, adult ADHD burnout is a lesser-known but no less important factor.
This article will define ADHD burnout, discuss why people with the illness may be more prone to it, and discuss warning signals, both physical and emotional. We will also offer some helpful coping mechanisms for ADD exhaustion.
A protracted state of extreme physical and mental exhaustion , known as burnout, is typically accompanied by a feeling of disappointment and alienation from daily or work-related activities. It typically occurs when people experience extreme exhaustion and overwhelm from handling excessive stress or responsibilities for an extended period of time.
Although burnout is not directly caused by ADHD, people with this disorder may be more likely to experience it. This is due to the fact that dealing with ADHD frequently necessitates extra mental and emotional work, which makes the everyday grind more taxing. The ongoing need to control one’s attention, impulses, and emotions can raise stress levels, which can exacerbate burnout if left unchecked.
Burnout from ADHD is typically overwhelming and perplexing for people. It entails a complicated interaction between the accumulated effects of stress and the cognitive difficulties related to the illness. Understanding the mental and physical symptoms ↗ that frequently accompany this chronic fatigue condition is crucial.

Burnout caused by ADHD can have particularly upsetting emotional symptoms. Nevertheless, they are a reaction to the particular difficulties presented by ADHD burnout rather than a reflection of personal failure.
The physical manifestations of ADHD burnout can be just as difficult to manage because they add to the already difficult task of ADHD management. It’s critical to identify and treat these bodily symptoms in order to effectively manage ADHD burnout and enhance general wellbeing.
Symptoms of ADHD burnout typically follow a pattern. When someone with ADHD experiences a burst of energy and enthusiasm, they usually start the cycle by taking on a lot of chores or projects. They often overcommit, taking on more obligations than they can reasonably handle, when their excitement peaks. Then, it could be harder for them to begin or complete these jobs that need concentration and effort, which could lead to feelings of tension, exhaustion, and overload. At this point, the subsequent phase of the ADHD burnout cycle begins.
People continue the cycle by using avoidance, procrastination, or self-care as a coping mechanism for their stress. At this point, they stop caring about their responsibilities and may withdraw to decompress, which could make them feel alone and inadequate. They eventually re-enter the cycle by taking on too much when they begin to heal.
Determining how ADHD burnout usually manifests in our daily lives is essential to effectively addressing it. These symptoms highlight the profound and varied ways that ADHD permeates different facets of life, impacting everything from relationships to the workplace. The first step in developing individualized remedies and starting a path toward better mental health is recognizing these symptoms.
Individuals with ADHD frequently attempt to withdraw and steer clear of social situations. There is a chance that this retreat will leave you feeling more alone and less mentally well. Having strong social ties is crucial since the loneliness that results can strain relationships and worsen emotional suffering.
People with ADHD may experience excessive stress, decreased productivity, and job dissatisfaction at work. These emotions may lead to conflicts with supervisors and coworkers, which could be detrimental to professional development and work relationships. The persistent challenges with maintaining focus and organization might heighten depressive symptoms, highlighting the necessity of encouraging work settings and coping techniques.
Individuals who are going through ADHD burnout may overlook their own needs, which can result in emotional and physical tiredness as well as an increased risk of illness. Neglect has a profound impact on mental health and can influence all aspects of life.
ADHD can cause elevated emotional states, which can impair relationships with loved ones by making people more prone to irritation and moments of grief or frustration. It can be difficult to navigate these emotional highs and lows; in order to preserve equilibrium and wellbeing, mindful approaches and emotional regulation skills are necessary.
Burnout can have an adverse effect on academic performance in the educational setting by lowering motivation, performance, and involvement in learning activities. Academic endeavors can be particularly difficult for people with ADHD due to their difficulty focusing and meeting deadlines. To meet their learning needs, a combination of assistance, accommodations, and customized tactics are needed.
While untreated ADHD symptoms have a major role in the development of ADHD burnout, a number of other factors also have a big impact. Here are a few possible causes of ADHD burnout.
Unmanaged ADHD symptoms increase the likelihood of burnout rather than decreasing it. Untreated symptoms combined with ongoing struggle can worsen people’s stress levels and make it more difficult for them to adequately manage life’s varied demands.
Managing a lot of work and deadline pressure can significantly increase stress levels in people with ADHD and serve as a trigger for burnout. Resilience can be weakened by the constant strain and the unrelenting speed, which makes handling everyday obligations even more difficult.
Burnout can result from a tendency to overlook one’s own needs due to taking on more than one can bear and a persistent desire to match others’ expectations. This disregard for oneself in an attempt to gain acceptance exacerbates inner conflicts and gradually depletes one’s wellbeing and energy.
Hiding symptoms of ADHD in order to fit in with society’s expectations can exacerbate internal conflicts and lead to burnout and tiredness . This ongoing disguising exacerbates psychological anguish, which leads to a severe sensation of exhaustion and powerlessness and makes people feel misinterpreted and alone.
Avoidance and procrastination are more than just poor habits. These are compounding stressors that raise the risk of burnout. Avoiding tasks causes tension and anxiety to build up over time, which makes you feel under pressure.
People who struggle with organization and time management may feel overburdened and exhausted. This inefficiency eventually contributes to burnout by causing overwhelm, depleting energy, and intensifying feelings of hopelessness and tiredness.
A higher risk of burnout might result from managing ADHD much more complicatedly due to a lack of understanding from friends, family, and coworkers. It also exacerbates emotions of miscommunication and loneliness, which makes managing ADHD more difficult.
For those with ADHD, structure and routine make it easier to focus and prevent fatigue by reducing confusion and ambiguity. As a result, the unpredictability and instability make it harder to stay focused, which accelerates the onset of burnout.
Using improper work habits increases stress and has a detrimental effect on mental health, which makes burnout more likely to occur. These unhealthy behaviors put people’s physical, mental, and emotional well-being at risk and drive them into burnout.
There are a number of tactics that can lessen the likelihood of experiencing ADHD burnout or lessen its symptoms. Among them are the following:
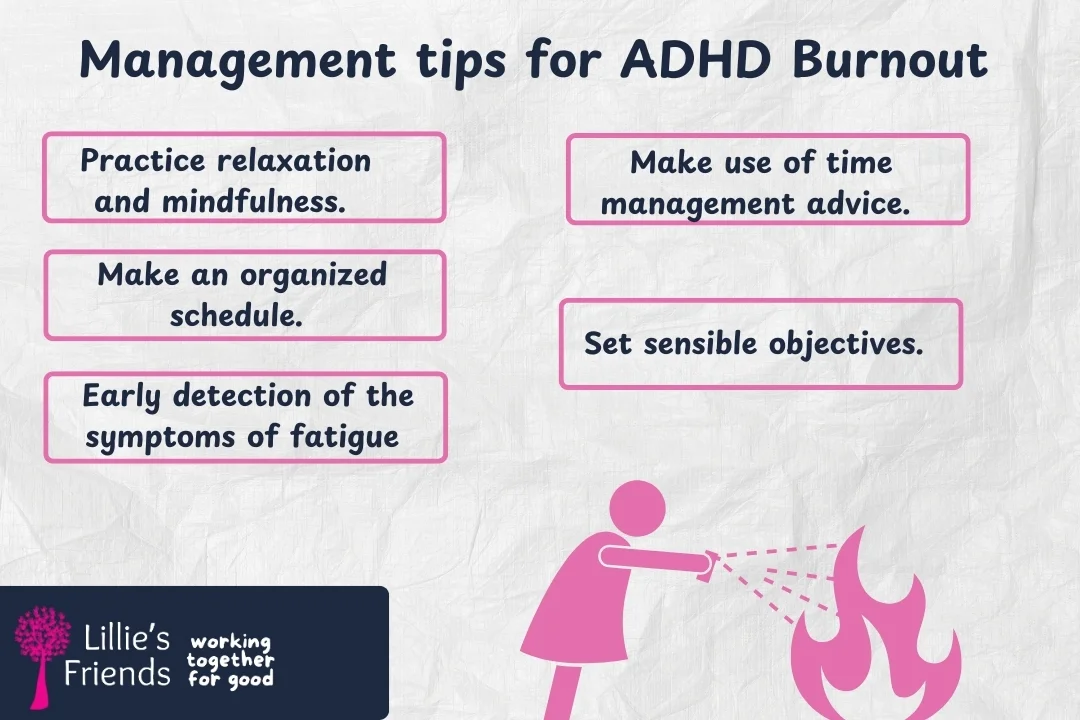
It takes a proactive strategy to overcome ADHD burnout. It’s not only about getting through the current burnout; it’s also about setting up a framework to keep it from happening again. These pointers function as a road map for healing, emphasizing self-care, establishing boundaries, and ongoing introspection to guarantee resilient and long-lasting healing.
In fact, coping with ADHD burnout is a difficult, continuous process. While ADHD burnout therapy places a strong emphasis on self-care and boundary setting, effective prevention of this mental health issue depends on structure, realistic goals, and a helpful supporting environment.
We recognize that coping with ADHD symptoms is an ongoing process of learning and adjustment; the steps below are meant to be a guide toward reaching mental health balance.

To distinguish between burnout and ADHD, speak with a medical expert. Some symptoms, like trouble concentrating and feeling overwhelmed, may be shared by several illnesses. But they have diverse causes, and their management may call for various strategies.

For an accurate diagnosis of depression or ADHD, get evaluated by a professional. Because some symptoms of ADHD, burnout, and depression overlap, separating them requires expert assessment.

Depending on coping strategies, degree of support, and individual characteristics, the duration of ADHD burnout might vary greatly. Without the right care and attention, it could linger for a few days for some people and several weeks or longer for others. A good diagnosis and treatment plan require consultation with a mental health specialist.

Trying to manage their symptoms can leave people with ADHD feeling more depleted and stressed than those without the disorder, which can lead to feelings of exhaustion and burnout.

Compared to men, women may be more prone to internalizing and hiding the symptoms of ADHD. This susceptibility is frequently brought on by particular stresses that women experience, such as obligations and expectations from society, which can result in chronic stress and an increased risk of burnout. Moreover, women with ADHD are frequently misdiagnosed or underdiagnosed, which results in a lack of care and support and increases their susceptibility to burnout. To get a firm understanding, more research is necessary as the evidence addressing the prevalence of ADHD burnout in women compared to men is inconclusive.